Introduction
The diamond industry has seen remarkable advancements over the past few decades, driven by technological innovation and a relentless pursuit of perfection. From traditional mining to sophisticated cutting techniques, the industry continues to evolve. This blog explores the latest innovations in diamond manufacturing and what the future holds for this sparkling sector.
The Current State of Diamond Manufacturing
Before diving into future innovations, it’s essential to understand the current landscape of diamond manufacturing. The industry today relies heavily on advanced technologies such as laser cutting, computer-aided design (CAD), and robotic automation. These technologies have significantly improved the precision, efficiency, and quality of diamond production.
Key Innovations in Diamond Manufacturing
1. Lab-Grown Diamonds
One of the most groundbreaking advancements in recent years is the production of lab-grown diamonds. These diamonds are created using high-pressure, high-temperature (HPHT) or chemical vapor deposition (CVD) methods, replicating the natural diamond formation process.
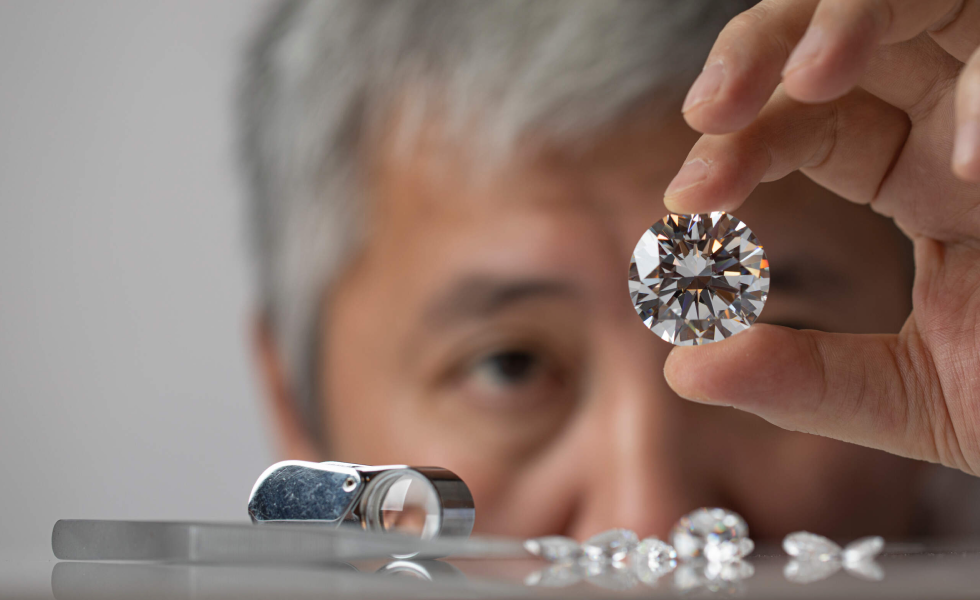

- Sustainability: Lab-grown diamonds are more environmentally friendly, reducing the need for extensive mining.
- Quality Control: These diamonds offer consistent quality and can be customized to specific requirements.
2. Advanced Laser Cutting
Laser cutting technology has advanced significantly, offering unprecedented precision and efficiency.
- Ultra-Fine Lasers: These lasers can make extremely precise cuts, enhancing the symmetry and overall quality of the diamond.
- Reduced Waste: Advanced lasers minimize material loss, ensuring more of the rough diamond is retained.
3. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing various stages of diamond manufacturing.
- Grading and Sorting: AI-powered systems provide consistent and accurate grading, reducing human error.
- Cutting Optimization: Machine learning algorithms can analyze rough diamonds and determine the optimal cutting strategy to maximize yield and quality.
4. 3D Printing
3D printing is making its way into diamond manufacturing, particularly in the creation of custom settings and molds.
- Customization: Allows for the creation of intricate and unique designs that were previously impossible.
- Prototyping: Rapid prototyping helps in designing and testing new cuts and settings efficiently.

5. Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is being used to enhance transparency and traceability in the diamond supply chain.
- Provenance Tracking: Ensures the authenticity of diamonds and helps combat issues like conflict diamonds.
- Consumer Confidence: Provides consumers with verifiable information about the origin and journey of their diamonds.Emerging Trends and Future Directions
Emerging Trends and Future Directions
1. Sustainable Practices
Sustainability is becoming a central focus in diamond manufacturing.
- Eco-Friendly Mining: Techniques such as marine mining and zero-impact mining are being explored.
- Recycling and Reuse: Innovations in recycling old diamonds and repurposing them into new jewelry pieces are gaining traction.
2. Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is poised to bring revolutionary changes to diamond manufacturing.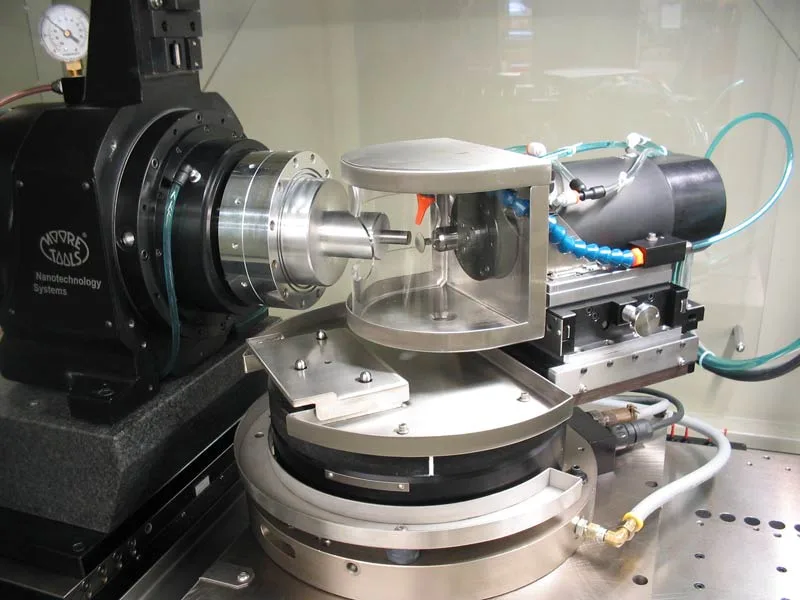
- Enhanced Properties: Nanodiamonds can be engineered to have superior hardness and thermal conductivity.
- Medical Applications: Potential uses in medical devices and treatments due to biocompatibility and unique properties.
3. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing holds the potential to transform various aspects of diamond manufacturing.
- Complex Simulations: Can simulate and optimize the diamond cutting process with unparalleled accuracy.
- Material Science: Aids in the development of new materials and technologies involving diamonds.
4. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies are enhancing the customer experience and manufacturing process.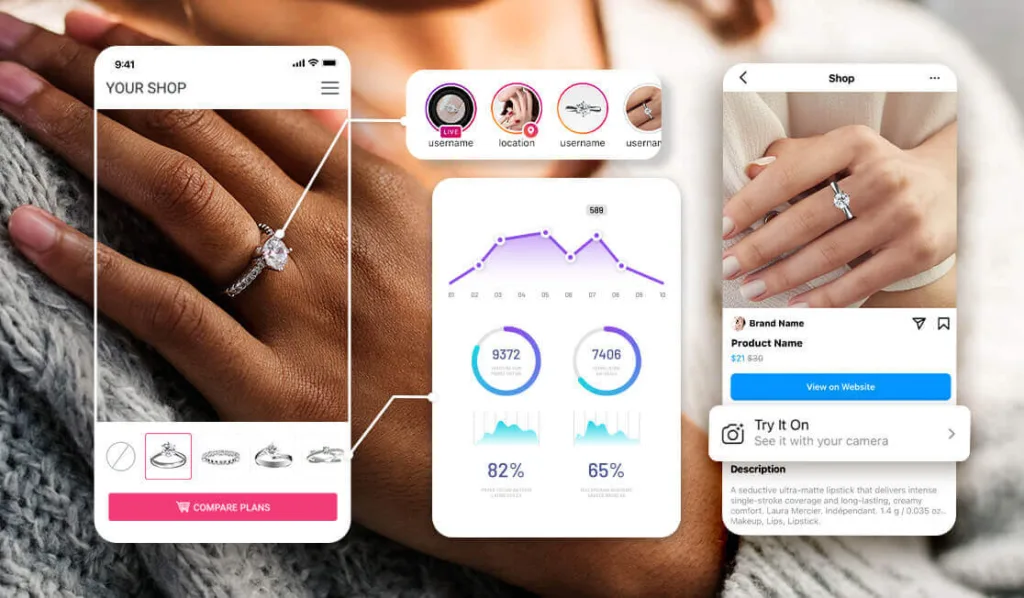
- Virtual Try-Ons: Allows customers to virtually try on jewelry, improving the buying experience.
- Training and Simulation: Provides immersive training for diamond cutters and inspectors, enhancing skills and precision.
Challenges and Considerations
While these innovations are exciting, they also bring challenges that need to be addressed:
- Cost: Advanced technologies can be expensive to implement, particularly for smaller manufacturers.
- Skill Development: The industry must invest in training workers to use new technologies effectively.
- Ethical Concerns: Ensuring that technological advancements do not exacerbate existing ethical issues in the industry.
Conclusion
The future of diamond manufacturing is bright, with numerous innovations poised to transform the industry. From lab-grown diamonds to AI and blockchain, these advancements promise to enhance efficiency, sustainability, and quality. As the industry continues to evolve, staying abreast of these trends will be crucial for manufacturers looking to remain competitive and meet the demands of a discerning market. By embracing these innovations, the diamond industry can ensure that it continues to shine brightly for generations to come.

